Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
IP and VRM#
Induced Polarization (IP) and Viscous Remanent Magnetization (VRM): Comparison of responses of a model with only conductivities, IP, VRM, and IP+VRM.
This example is based on a contribution from Nick Williams (@orerocks).
import empymod
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.constants import mu_0
plt.style.use("ggplot")
Survey Setup#
Loops#
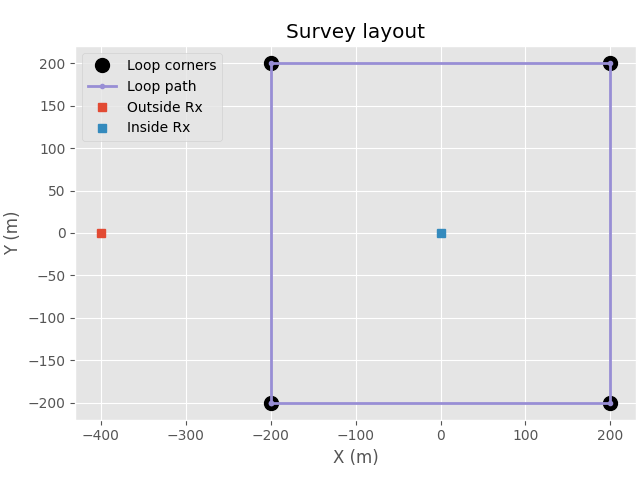
Create a square loop source of 400 x 400 m, and two Z-component receivers, one outside and one inside the loop; all at the surface (z=0).
Note: Take care of the direction of the loop; defining it counterclockwise will yield responses that are opposite (factor -1) to a loop defined clockwise (following Farady’s law of induction).
# Src: x0, x1, y0, y1, z0, z1
src_x = np.array([-200, -200, 200, 200, -200])
src_y = np.array([-200, 200, 200, -200, -200])
src_dipole = [src_x[:-1], src_x[1:], src_y[:-1], src_y[1:], 0, 0]
# Rec: x, y, z, azm, dip
rec = [[-400., 0], [0, 0], [0, 0], 0, 90]
# Plot the loop
fig, ax = plt.subplots(constrained_layout=True)
# Source loop
ax.plot(src_x[:-1], src_y[:-1], "ko", ms=10, label="Loop corners")
ax.plot(src_x, src_y, "C2.-", lw=2, label="Loop path")
# Receiver locations
ax.plot(rec[0][0], rec[1][0], "s", label="Outside Rx")
ax.plot(rec[0][1], rec[1][1], "s", label="Inside Rx")
ax.set_xlabel("X (m)")
ax.set_ylabel("Y (m)")
ax.set_title("Survey layout")
ax.legend()
ax.set_aspect("equal")
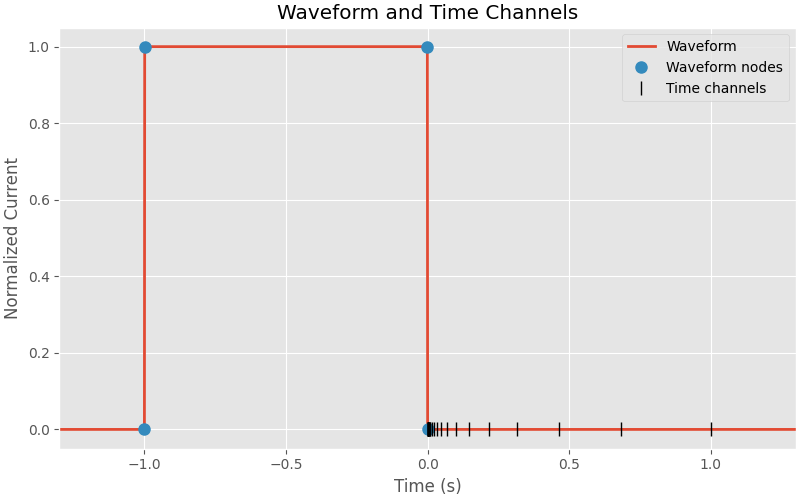
Trapezoid Waveform#
# On-time negative, t=0 at end of ramp-off
# Quarter period for 50 % duty cycle
source_frequency_hz = 0.25
on_time_s = 1 / (source_frequency_hz * 4)
# Time channels: off-time only, positive times
# 25 channels from 0.1 ms to 1000 ms for 0.25 Hz 50 % duty cycle
times = np.logspace(-4, np.log10(on_time_s), 25)
# Waveform
nodes = np.array([-1, -0.999, -0.001, 0])
amplitudes = np.array([0., 1, 1, 0])
print(
"Waveform details:\n"
f" Time channels: {len(times)} channels "
f"from {times[0]*1000:.2f} ms to {times[-1]:.2f} s (all off-time)\n"
" Waveform:\n"
f" On-time from {nodes[0]:.1f} s to {nodes[3]:.1f} s\n"
f" Ramp on: {nodes[0]*1e3:.1f} to {nodes[1]*1e3:.1f} ms\n"
f" Ramp off: {nodes[2]*1e3:.1f} to {nodes[3]*1e3:.1f} ms\n"
)
Waveform details:
Time channels: 25 channels from 0.10 ms to 1.00 s (all off-time)
Waveform:
On-time from -1.0 s to 0.0 s
Ramp on: -1000.0 to -999.0 ms
Ramp off: -1.0 to 0.0 ms
Plot waveform and time channels
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(8, 5), constrained_layout=True)
# Waveform
ax.plot(np.r_[-1.5, nodes, 1.5], np.r_[0, amplitudes, 0],
"C0-", lw=2, label="Waveform")
# Nodes
ax.plot(nodes, amplitudes, "C1o", markersize=8, label="Waveform nodes")
# Mark time channels
ax.plot(times, np.zeros(times.size), "k|", ms=10, label="Time channels")
# Formatting
ax.set_xlabel("Time (s)")
ax.set_title("Waveform and Time Channels")
ax.set_ylabel("Normalized Current")
ax.set_xlim([-1.3, 1.3])
ax.legend()
Viscous Remanent Magnetization (VRM)#
This function implements the following VRM model
where \(\chi\) is the viscous susceptibility.
def vrm_from_mu(inp, p_dict):
"""
Isotropic VRM hook for empymod using mu-per-layer.
Implements a log-uniform relaxation distribution over [tau1, tau2].
Inputs expected in `inp` (all per-layer arrays):
- mu : baseline permeability (absolute). Exp. to be pre-mult. by mu_0
- dchi : amplitude of viscous susceptibility (dimensionless)
- tau1 : lower bound of relaxation times [s]
- tau2 : upper bound of relaxation times [s]
"""
# Frequencies (nf,)
freq = np.atleast_1d(p_dict["freq"])
jw = 2j * np.pi * freq[:, None]
# Per-layer inputs (nl,)
mu = np.atleast_1d(inp["mu"]) # required
dchi = np.atleast_1d(inp.get("dchi", 0.0))
tau1 = np.atleast_1d(inp.get("tau1", 1e-10))
tau2 = np.atleast_1d(inp.get("tau2", 10.0))
# Log-uniform increment term
ln_ratio = np.log(tau2[None, :] / tau1[None, :])
incr = (1.0 - np.log((1.0 + jw * tau2[None, :]) /
(1.0 + jw * tau1[None, :])) / ln_ratio)
# Frequency-dependent relative permeability and zeta
zeta = jw * (mu[None, :] + mu_0 * dchi[None, :] * incr)
return zeta, zeta # Horizontal and vertical the same
Pelton Cole-Cole#
This function implements the following Pelton Cole-Cole IP model for the resistivities
where \(m\) is the intrinsic chargeablitiy. For more information on the Cole-Cole model refer to the IP example; note that this model is slightly different from the one presented there.
def pelton_cole_cole_model(inp, p_dict):
"""
Pelton et al. (1978) Cole-Cole IP model.
Inputs expected in `inp`:
- res : DC resistivity (Ohm-m)
- m : intrinsic chargeability (V/V), 0 <= m < 1
- tau : time constant (s)
- c : frequency dependency, 0 < c < 1
Returns complex electrical conductivity (etaH, etaV).
"""
# Compute complex resistivity from Pelton et al.
iotc = np.outer(2j * np.pi * p_dict["freq"], inp["tau"]) ** inp["c"]
# Version using equation 16 of Tarasov & Titov (2013)
rhoH = inp["res"] * (1 + inp["m"] / (1 - inp["m"]) / (1 + iotc))
rhoV = rhoH * p_dict["aniso"] ** 2
# Add electric permittivity contribution
etaH = 1 / rhoH + 1j * p_dict["etaH"].imag
etaV = 1 / rhoV + 1j * p_dict["etaV"].imag
return etaH, etaV
Subsurface Model#
loop_current = 1.0
inp = {
"src": src_dipole,
"rec": rec,
"depth": [0.0, 50.0],
"freqtime": times,
"signal": {"nodes": nodes, "amplitudes": amplitudes, "signal": -1},
"srcpts": 10,
"msrc": False,
"ftarg": {"dlf": "key_81_2009"},
"htarg": {"dlf": "key_101_2009", "pts_per_dec": -1},
"verb": 1,
}
param_ip = {
"m": np.array([0.0, 0.05, 0.15]),
"tau": np.array([0.0, 0.005, 0.02]),
"c": np.array([0.0, 0.4, 0.6]),
}
param_vrm = {
"dchi": np.array([0.0, 0.005, 0.02]),
"mu": np.array([mu_0, mu_0 * 1.05, mu_0]),
}
# Build empymod model dict with VRM and/or Cole-Cole hooks as needed
res = np.array([2e14, 1.0, 100])
res_vrm = {"res": res, "func_zeta": vrm_from_mu, **param_vrm}
res_ip = {"res": res, "func_eta": pelton_cole_cole_model, **param_ip}
res_both = {**res_vrm, **res_ip}
Compute responses#
# Store results and timing for each model
results = {}
for compute_B_field in [True, False]:
# Source strength depends on output field type
# For B field: mu_0 * current returns B in frequency domain
# For dB/dt: just current, then multiply by i*omega*mu_0 later
inp["mrec"] = True if compute_B_field else "b"
inp["strength"] = mu_0 * loop_current if compute_B_field else loop_current
out = {}
# Conductivity
out["σ"] = empymod.bipole(**inp, res=res).sum(axis=-1)
# IP
out["IP"] = empymod.bipole(**inp, res=res_ip).sum(axis=-1)
# VRM
out["VRM"] = empymod.bipole(**inp, res=res_vrm).sum(axis=-1)
# IP + VRM
out["IP+VRM"] = empymod.bipole(**inp, res=res_both).sum(axis=-1)
results["B field" if compute_B_field else "dB/dt"] = out
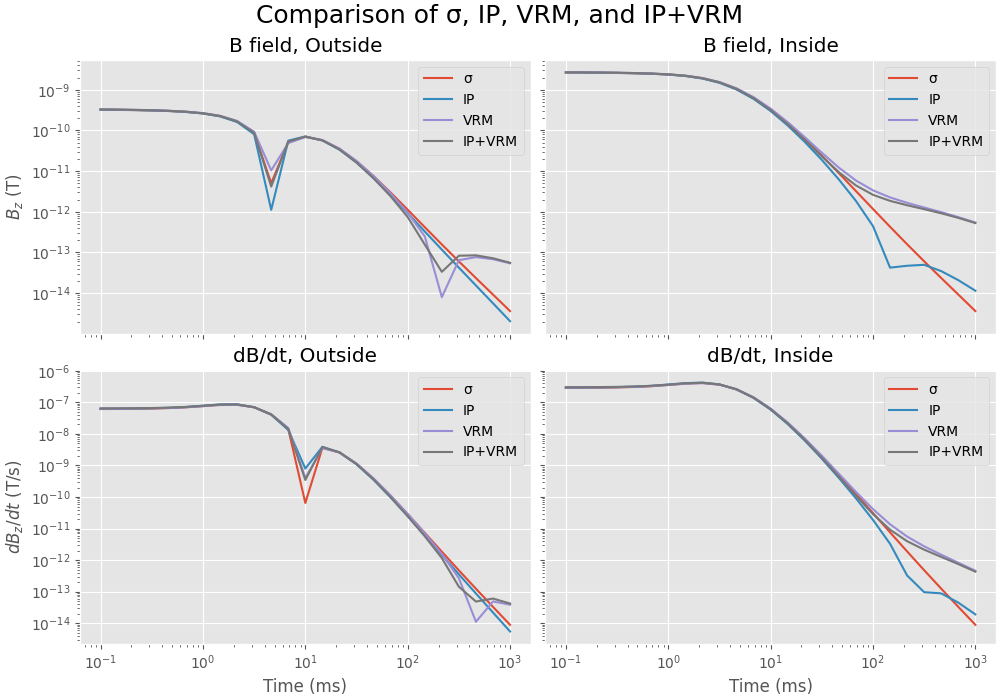
Plot results#
fig, axs = plt.subplots(
2, 2, figsize=(10, 7), sharex=True, sharey="row", layout="constrained"
)
in_out = ["Outside", "Inside"]
# Loop over B-field - dB/dt
for i, compute_B_field in enumerate(["B field", "dB/dt"]):
result = results[compute_B_field]
# Loop over outside - inside loop
for ii in range(2):
# Loop over cases
for k, v in results[compute_B_field].items():
axs[i, ii].loglog(times*1e3, np.abs(v[:, ii]), label=k)
axs[i, ii].set_title(f"{compute_B_field}, {in_out[ii]}")
axs[i, ii].legend()
for ax in axs[1, :]:
ax.set_xlabel("Time (ms)")
axs[0, 0].set_ylabel("$B_z$ (T)")
axs[1, 0].set_ylabel("$dB_z/dt$ (T/s)")
plt.suptitle("Comparison of σ, IP, VRM, and IP+VRM", fontsize=18)
plt.show()
empymod.Report()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 7.732 seconds)
Estimated memory usage: 193 MB